Happy Summer Solstice Week! Let’s head to the lake!
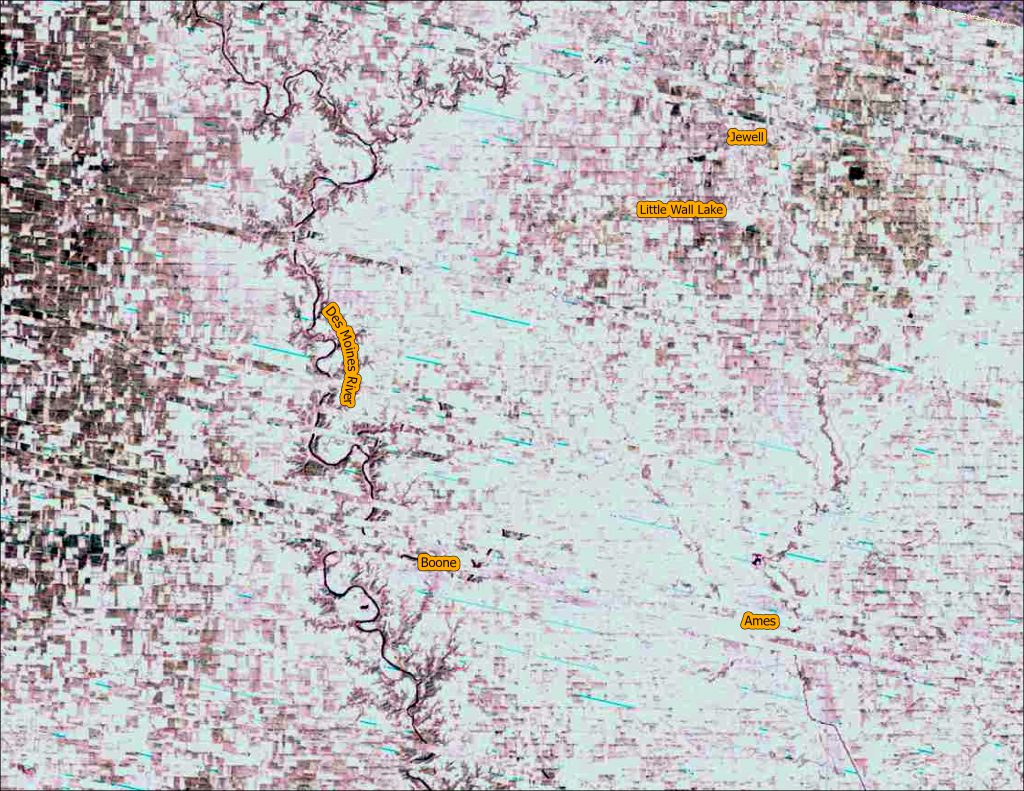
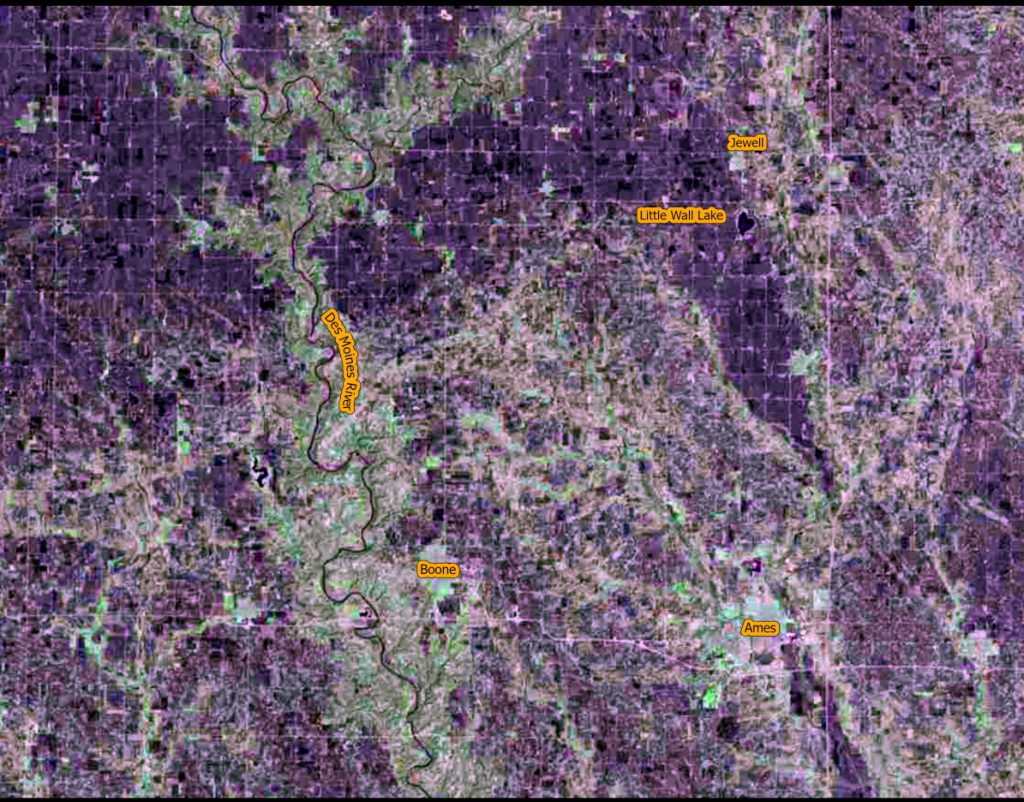
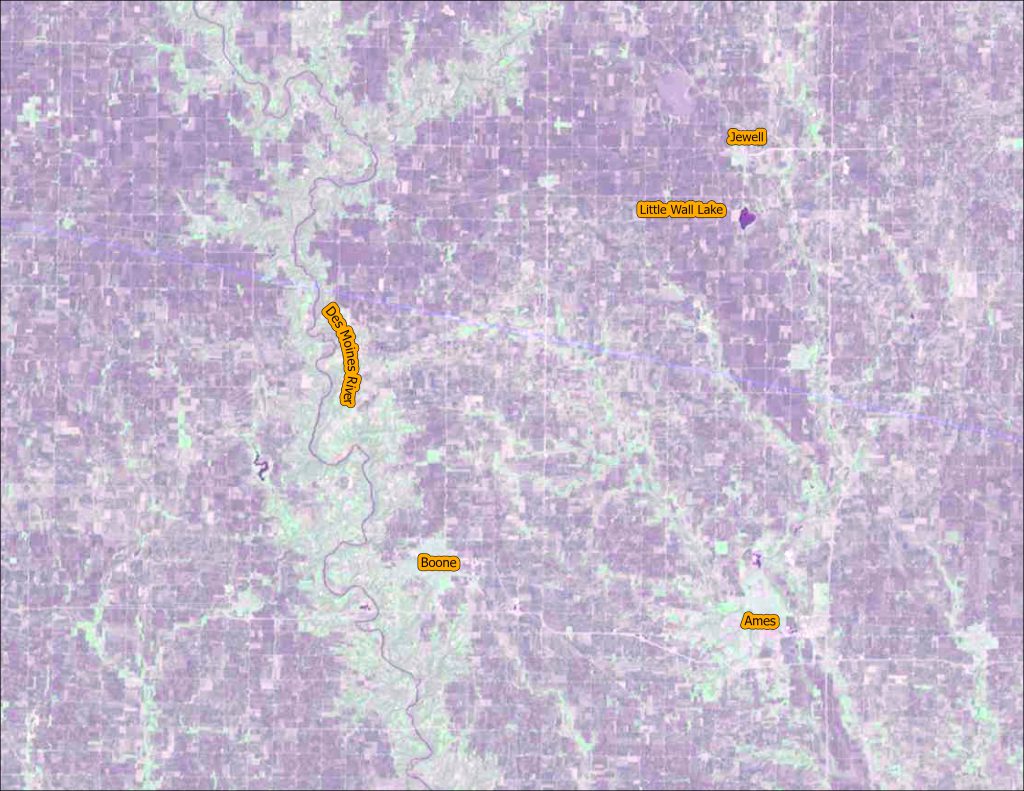
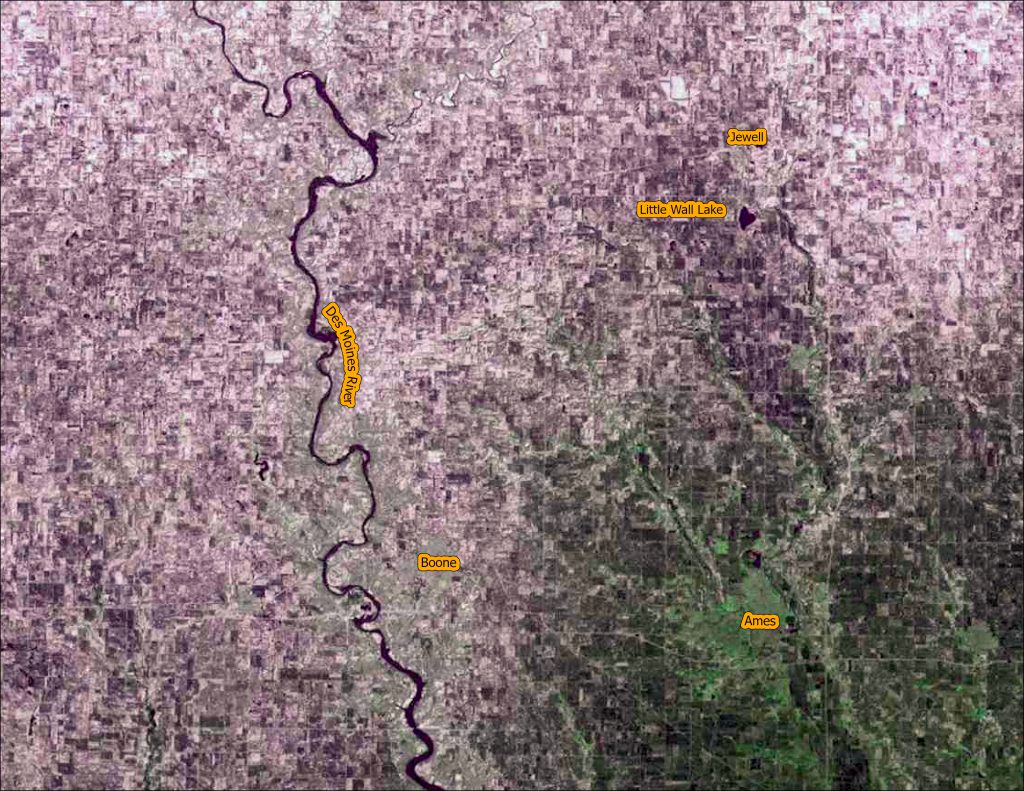
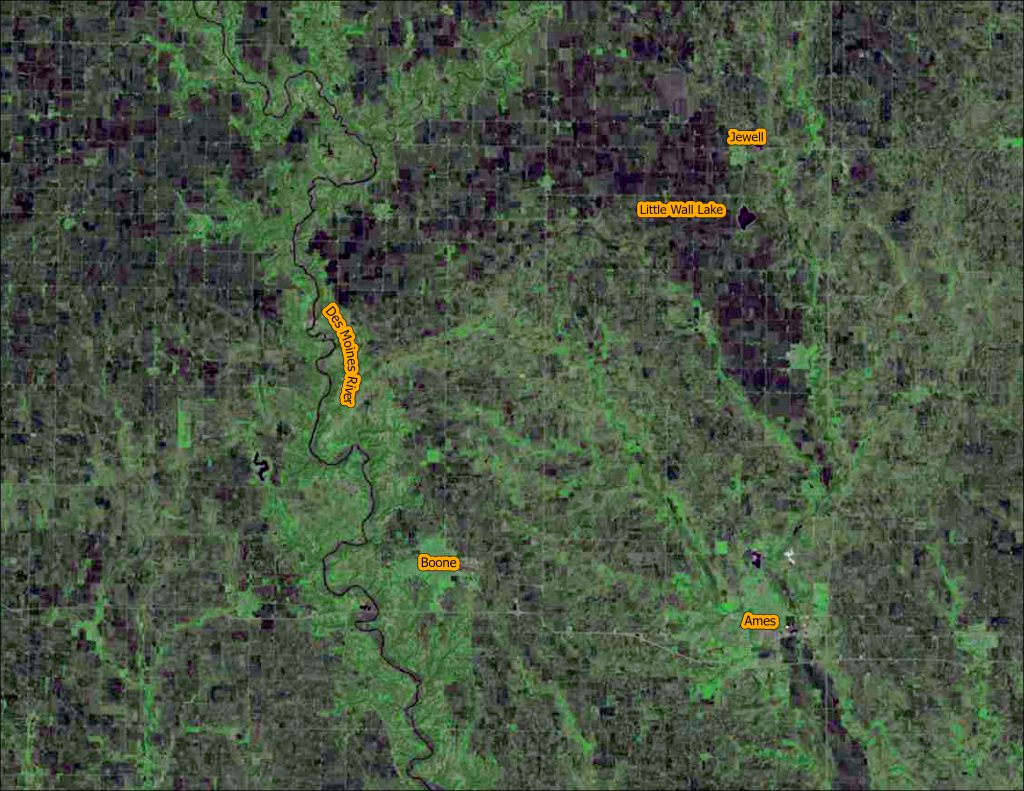
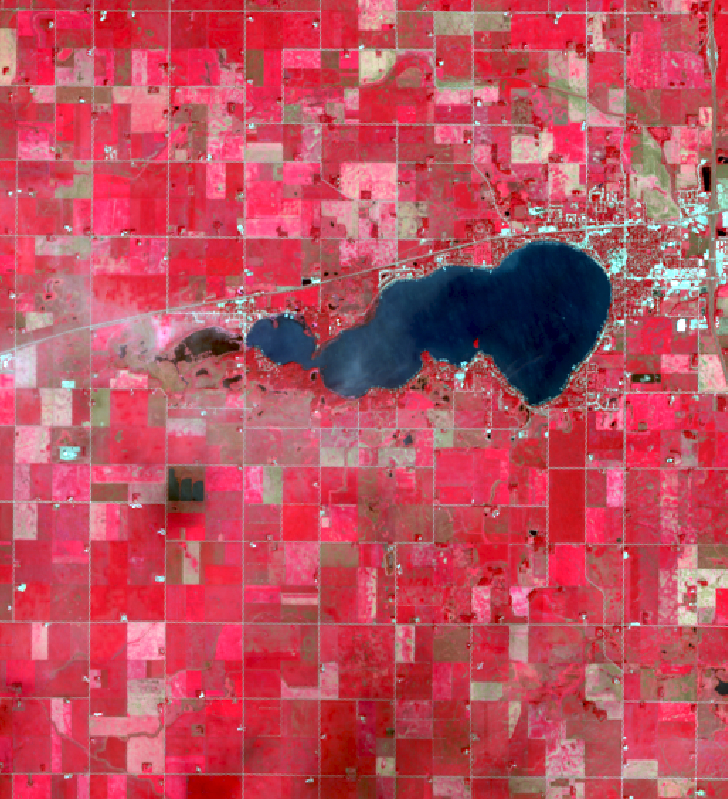
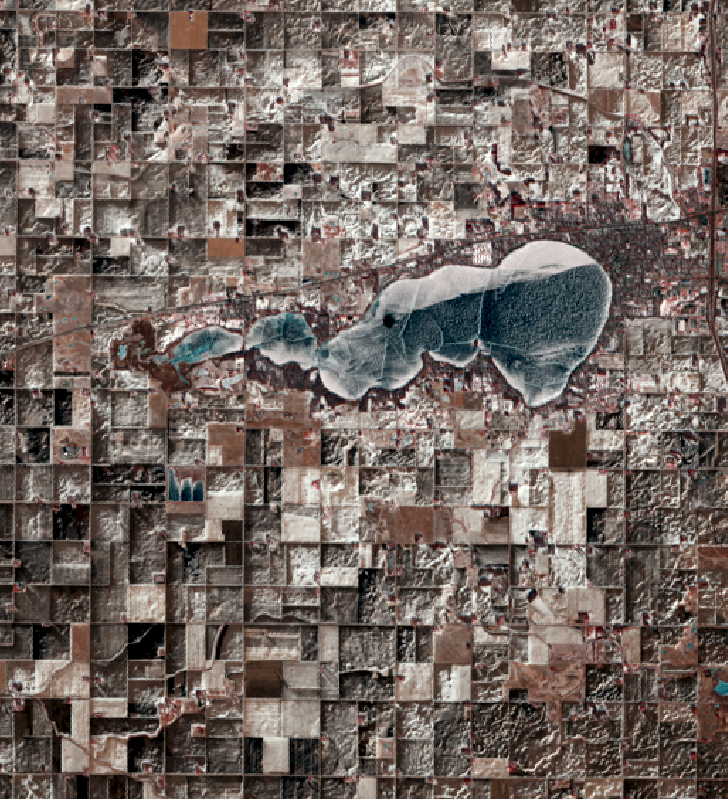
We are continuing our celebration of the 50th year of the US Landsat satellite imagery program. This week we are heading to the lake – Clear Lake, Iowa, located in north central Iowa.
Below are four images showing Summer Solstice (6/13/2019), Fall Equinox (9/17/2019), Winter Solstice (12/22/2019), and Spring Equinox (3/18/2019) from Landsat 8. The images are presented in color infrared which shows vegetation in red rather than green for better contrast.




Observations:
- At Summer Solstice things are still greening up while at Fall Equinox the fields are all green and some are beginning to be harvested.
- Observe the different states of the lake: open water, snow covered, and frozen.
- The topography of the landscape (ie. hills and roughness) are much more apparent with snow on the ground. In the summer/fall images, it all looks flat.